Typhoid Fever Explained with PPT
Topic Covered for Typhoid Fever
Typhoid is a serious illness that can leave you feeling very ill. This is like the worst possible flu. This illness can make you extremely ill. Tiny creatures called bacteria are the cause of typhoid.
The bacteria that cause typhoid fever are so tiny, you cannot see them without a magnifying glass. Typhoid-causing bacteria is known as Salmonella Typhi Just like animals, bacteria are also different. Salmonella Typhi causes the disease. In places with poor systems of waste disposal and water purification, typhoid is more prevalent.
In areas where garbage isn’t properly disposed of and water isn’t clean, this disease is more common. It’s important to maintain good sanitation in order to prevent typhoid.
Two Different Kinds of Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever:
Reason: most generally happens because of the bacteria Salmonella Typhi.
Spread: This virus is spread by contaminated water or food, normally because of bad health methods.
Symptoms:
High high temperature is a heat (typically over 103degF, or 39.4 degC).
Frustration
Discomfort in the abdomen
Weaknesses and exhaustion
Constipation and diarrhea
Rose spots on upper body and abdomen.
The intensity of typhoid can vary from mild to major. It can create extreme complications, such as blood poisoning or intestinal tract perforation.
Treatment: Typhoid is frequently treated with anti-biotics.
Avoidance:
Tourists to areas with native to the island conditions need to be vaccinated.
Food and Water Safety Practices
Paratyphoid Fever:
Cause: Paratyphoid fever is caused by a different strain of Salmonella bacteria called Salmonella Paratyphi.
Similarities:
Transmission through contaminated food or water
Symptoms resembling typhoid fever (fever, abdominal discomfort, weakness).
Differences:
Milder Symptoms: Paratyphoid fever tends to have milder symptoms compared to typhoid fever.
Less Severe Course: While it can cause illness, it is generally less severe than typhoid fever.
Treatment and Prevention:
Similar to typhoid fever, antibiotics are used for treatment.
To prevent the spread of illness, it’s important to practice good hygiene and steer clear of food and water that may be contaminated.
How You Feel When You Have Symptoms?
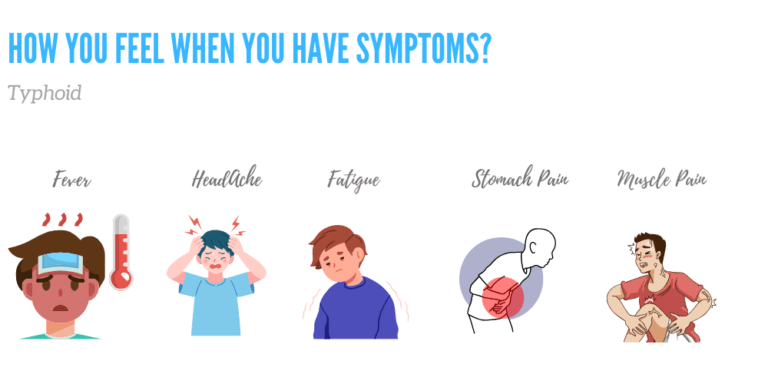
Early signs of typhoid fever include gradually increasing fever, persistent headaches, weakness and fatigue, muscle aches, stomach pain, and digestive disturbances like diarrhea or constipation.
Some may also develop rose spots on the abdomen and chest. In the later stages of the disease, individuals may experience intestinal problems, persistent abdominal discomfort, a swollen stomach, sepsis in severe cases, and neurological symptoms such as mental confusion and difficulty reacting to surroundings.
Diagnostic tests in Typhoid
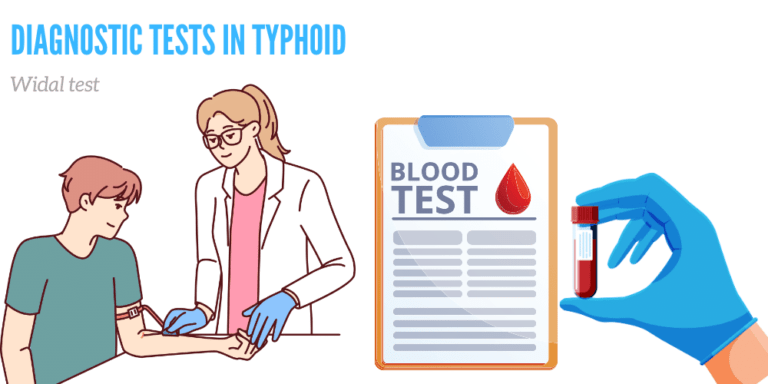
The Widal test is a serological diagnostic test used to identify the presence of infection with Salmonella typhi or Salmonella paratyphi bacteria, which cause typhoid fever. It assesses the level of antibodies produced by the body in response to these bacterial infections. During the test, a blood sample is mixed with an antiserum containing antibodies against the bacteria. If antibodies are present, they react with the antiserum, causing agglutination (clumping) of red blood cells. A positive Widal test indicates an ongoing or prior infection with the bacterium. This test is crucial for diagnosing current or recent typhoid infections and determining an individual’s immunity status.
Fever Investigations and CBC:
- Fever can be a manifestation of various infectious diseases, some of which can be life-threatening. However, clinical findings alone may not always pinpoint the exact cause.
- Laboratory diagnostics play a crucial role in early diagnosis and treatment planning. Among these, a CBC is commonly included in initial fever investigations.
- The CBC provides valuable information about blood cells and their characteristics. It’s a cost-efficient tool that assists clinical assessments.
Why CBC Matters:
- Different infections can have diverse effects on blood cells. Additionally, other non-infectious causes of fever may not significantly impact blood cell counts.
- Therefore, a CBC, along with other general infection biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP), is used to assess febrile patients early on.
CBC :
- Here’s how CBC helps:
- Leukocyte Count: Typhoid fever often leads to an increase in white blood cells (WBCs). However, this is not specific to typhoid and can occur in other infections too.
- Platelet Count: While not exclusive to typhoid, a low platelet count can raise suspicion.
- CRP Level: Elevated CRP levels may indicate inflammation but are not specific to typhoid.
- Blood Culture: A blood culture during the first week of fever can directly detect S. Typhi bacteria.
- ELISA Blood Test: This test looks for antibodies against S. Typhi.
- Here’s how CBC helps:
How Doctors Help to Cure Typhoid Fever?
- Antibiotics: These powerful medications target and kill the bacteriaresponsible for typhoid fever. They play a pivotal role in reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting recovery.
- Individualized Treatment: The choice of antibiotic depends on several factors:
- Severity: Mild cases may respond well to oral antibiotics, while severe cases might require intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
- Resistance Patterns: Local resistance patterns guide antibiotic selection. Some common antibiotics include ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, and ceftriaxone.
- Patient Health: The patient’s overall health, age, and any underlying conditions influence the choice.
- Adherence Matters: Completing the full course of antibiotics is critical. Stopping early can lead to relapse or the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains. Patients must follow their doctor’s instructions diligently.
How to Avoid Getting Typhoid Fever
- Street Food: Avoid consuming food from street vendors. It may not be hygienic .
- Filtered Water Only: Opt for properly filtered water. Clean water is crucial for preventing infections.
- Stay Clean: Prioritize personal hygiene, especially if you’re near someone with typhoid fever. Frequent handwashing is essential.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to maintain hydration.
- Handwashing: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This simple practice helps prevent the spread of germs.
- Consider Vaccination: If you’re heading to an area where typhoid fever is prevalent, think about getting vaccinated. This specialized medicine boosts your body’s defense against the disease-causing bacteria.
Conclusion

Typhoid fever is a serious illness that needs to remain treated correctly away. If you think you might have typhoid fever, you should go to a doctor as in the near future as you can. With the right treatment, you can get more desirable. And by taking some simple steps, you can avoid getting typhoid fever in the initial place. Stay safe and healthy!.